Explain Your Ethical Decision Making Process When Determining Your Answer Regarding Baby M
iii Upstanding Decision Making
The purpose of this affiliate is to:
- 1) Outline the decision making procedure
- 2) Explain the nature of ethical determination making
- 3) Provide ethical frameworks used in making decision making
Conclusion Making
This chapter introduces u.s.a. to the concept of ethical decision making. To properly contextualize our understanding of ethical decision making, maybe it would be prudent to separate the 2 elements – decision making in general, so ethics. Managers make thousands of decisions every day. In most cases they intuit the decision making process and can come to the best solution within nanoseconds of hearing almost a problem. These are the types of problems that are routine, and accept depression consequences. Nevertheless, the big decisions that managers have to regularly make require more due diligence, forethought, and collaborative effort with colleagues. These problems portend serious consequences, and in many cases organization operation depends on good decision making. Hannaway (1989) found that managers are in a constant state of making decisions as "[they] switch ofttimes from task to chore, changing their focus of attention to reply to issues every bit they arise, and engaging in a large volume of tasks of short duration" (p. 39).
Decision making is the activeness or procedure of thinking through possible options and selecting one (Brilliant et. al, 2019). A rudimentary framework for how managers appoint in the decision making procedure contains four steps.
- 1) Identify the problem
- 2) Generate alternatives
- 3) Decide on a form of action
- four) Implement
There are several ways that a manager tin can use this framework to make decisions – intuition, assay, democratic process, etc. Yet, they all comprise the same elements of problem identification and and so evaluating alternatives before deciding on a course of action. The intuitive decision maker simply "knows" what the problem and alternatives are before acting. A managing director using belittling tools might uncover new insights from trying to really figure out what the problem is. A autonomous manager volition rely on the utilise of the squad to work through understanding the problem and figuring out alternative courses of action.

Place the Problem
The kickoff claiming in decision making is working to understand what the problem is. Ineffective managers focus on the symptoms without identifying the underlying bug. A child with a runny nose does not have a runny nose problem, she has an infectious disease causing a running olfactory organ. The implication here is uncomplicated; if we treat symptoms, the problem will re-create the symptoms if given plenty fourth dimension. For the kid, let'due south say we stuff endless Kleenex upwards her olfactory organ. This won't address the virus creating this symptom and others (temperature, cough, etc.) In a similar fashion, a house might have a turnover issue and put resource towards paying people more than, improving conditions, or added benefits. However, without truly agreement the cause of the turnover, these resource are wasted. The turnover in this scenario is beingness caused past an unbearable manager that makes life miserable for employees. No amount of pay enhance or work condition changes will keep someone around for very long when abuse like this is happening.
A college freshman turns his paper in to the professor during the first week of class. A week later the professor calls the pupil into her function and states simply "Yous got a D on the paper, merely I have good news. You don't have a writing problem." The educatee is confounded, and asks the professor to explain. "Yous don't in fact take a writing problem, you have a reading problem. You write like you speak, which tells me that you do not read very much. I recommend that you read more than. Anything you lot want, simply read – Men'south Health, your textbook, Dostoevsky, and this will make you a better writer. You will naturally imitate what you lot are seeing." A good manager tries to understand what is causing the symptoms. First pace is to identify the existent problem.
Generate Alternatives
Problems come in different scopes and magnitude. In some cases they are routine, similar a director putting together a shift schedule for the calendar week. The problem identification is but a matter of understanding that personal preferences and personal obligations volition disharmonize equally he tries to schedule shifts. This problem does not require the managing director to generate a wide listing of alternatives. It might include negotiation, assuasive workers to swap shifts, or simply making a schedule and forcing employees to deal with it. Even so, there are bigger bug that crave a manager to generate a long and comprehensive list of alternatives. When issues have intense consequences, or the context is an unknown one to the organization, a wide list of alternatives is necessary. The future is unknown, and the trouble is unlike one you've ever seen. This is the time to brainstorm, become artistic, and generate alternatives.
Consider a visitor dealing with the aftermath of a mass shooting incident. Consider a fast food restaurant trying to remain solvent during a national pandemic that requires consumers to remain at dwelling. Consider a visitor in New Mexico who screens task applicants for drug use, and they are taking job applicants from Colorado where marijuana use is legal. Consider an plane manufacturer who lost consecutive contract bids and has to cutting expenses somewhere. Each of these problems are serious that crave managers to generate a broad list of alternatives.
If we see a problem we take seen before, we don't demand to stray as well far to observe viable alternatives. Nevertheless, when we face a new trouble in an unknown context, we need a wide range of alternatives. Here's a elementary illustration. Consider the following three questions:
Provide a range of outcomes (low and high estimates) for the following questions:
How many US Presidents accept resided in the White House?
What is the population of Reykjavik?
How many Sasquatches per square mile reside in the Pacific Northwest?
If you have whatsoever frame of references for these questions, your range of outcomes volition probably be narrow. If you have no idea, you demand to answer the question with a wide range. Most of us take a general idea that the number of total US Presidents is somewhere in the forties, and perhaps nosotros tin can think from a high school American History class that the British burned the White House during the War of 1812, which was probably iv to v presidencies in, and the White House has existed at to the lowest degree since then. This ways we tin estimate that the range is 35-45 presidents have lived there (The first was John Adams, making the correct respond 44). Reykjavik is in Republic of iceland, and if you knew that you lot also know it has a small population, and the city probably does not scissure the world's top 100 most-populated cities. It sort of feels like an Cheyenne, Wyoming or a Madison, Wisconsin – plenty to be a upper-case letter city, but non enough to brand headlines regularly. We might give this a wider range because we are non quite sure – 50,000 to 500,000 residents. The population of Reykjavik, Iceland is 125,000. Finally, those dang sasquatches. If you have a solid frame of reference, I would like to hear information technology, or maybe the government has already talked to you. . . . just alas most of us have merely theories and speculation (similar if there actually were sasquatches, don't you think your Uncle Howard who lives in Western Oregon would have shot one by at present?) We should give this question a VERY wide range of estimates. Let's use 0 to i,000. This is an unknown, with no frame of reference.
These 3 questions become progressively farther from any frame of reference yous have, which requires you to aggrandize your range of outcomes. This exercise illustrates the point that if nosotros take a frame of reference, we don't have to stray besides far. If we are in unchartered waters, we need to widen our thinking. The aforementioned holds true for problems and generating alternatives. We need to take the time to retrieve through all available options, and maybe fifty-fifty exercise something nosotros never thought possible, or has ever been done before.
Determine and Implement
Once we have generated a list of alternatives, nosotros need a fashion to decide which of the alternatives should be pursued. Over again, managers tin can use intuition, analysis, or commonwealth to achieve this. Nevertheless, a mutual approach is the employment of a toll do good analysis. The cost-benefit assay is a process by which managers evaluate a class of action based on the anticipated positive and negative effects an alternative will generate. In fiscal analysis the calculations tin be quite complicated, but one time you have an output the decision is like shooting fish in a barrel – cull the project with the highest rate of return or net present value. However, when making decisions that are more than difficult to quantify, a price benefit assay becomes more challenging. The costs can include any form of utility – upper-case letter expenditures, employee morale, loss of homo life, a decrease in customer service, environmental pollution, violation of the law. The benefits are equally difficult to gauge and in many cases – revenues, company civilisation, respect to human dignity, customer rapport, environs stewardship, and avoidance of fines. Once the cost benefit analysis is conducted, the decision becomes clear, and this is the third step in the decision making process.
A example of this toll benefit analysis – Tara, the regional sales managing director has to decide whether terminating her all-time salesman is in the best interest of the company. Braden is the meridian performer by far in the organization. Withal, he treats the accounting squad with disdain, the logistics team hates him, and he sometimes engages in deliberately rebel behavior. Keeping him around would bolster sales figures for the foreseeable future, but the company will slowly leak some adept talent away as Braden's coworkers find a place to piece of work with better workplace civilization. Firing Braden comes with the benefits of retained talent in support services, improved morale, and a clear precedent for futurity salesmen, that this beliefs won't be allowed. The cost benefit analysis results in a decision to terminate, and to eat the costs of preparation a new rent, and working for a few months to go sales figures dorsum up.
Once the alternatives are evaluated and i (or more) are selected, implementing the course of action requires the director to put resources towards that option. This could mean signing a check, empowering an employee to have on responsibility, or in the example above, calling William into the office to communicate a conclusion has been fabricated.
Ethical Dilemmas
Most decisions that managers make during the solar day are routine and do non involve the need to reflect on the ideals of the state of affairs. Still, the steps in the decision making framework need to exist followed especially stringently in the situations where upstanding implications loom. This begs the question – which situations present ethical dilemmas to managers?
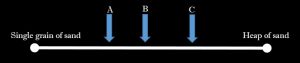
Before we answer that question, let'southward infringe some thinking from the Ancient Greeks. Socrates posed the question – "If we between us, have a heap of sand, consisting of millions of grains, and suppose I remove 1 grain, shall information technology no longer exist a heap?" This question then follows, "supposing no, shall I remove ii grains and then that information technology no longer becomes a heap?" This logic follows until only ane grain remains, at which point we would no longer consider the heap of sand a heap. However, is there a point betwixt one and a million, that we tin can identify the heap as something other than a heap? Socrates termed this a "Sordite'southward Paradox." That is, a minor change in the status of being does not modify the existence, simply a serial of consecutive modest changes would modify its beingness. How does this apply to ethical dilemmas?
Ethical dilemmas are situations that present various courses of moral action, none of which are clearly acceptable or preferable. This ways that the upstanding solution is non clear, yet a option needs to be made. Nether this definition we need to exclude decisions like adulterous a customer, lying to the shareholders, polluting rivers, embezzling, money laundering, ignoring unsafe weather condition, putting the public at risk, insurance fraud, extortion, blackmail, copyright violations, and the long list of other white-collar crimes. These are not ethical dilemmas. These are ethical choices whereby we choose to do right or the incorrect. The difference betwixt these and ethical dilemmas is that the choice in a dilemma is non always articulate. Allow'southward go back to Socrates to explore this.
Socrates tells us that at one betoken the sand heap is a heap, and at some point the heap becomes something less than a heap. There exists a gray surface area inside the change, a indicate that determines whether or not it's a heap, simply that bespeak is unclear. If you wait at Effigy ii.one, at which point (A, B, or C) does the sand no longer represent a heap.
Figure 3.1 – A Sordite'south Paradox
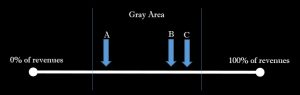
Let'south utilize this to an ethical dilemma (remember, it's a determination with a grayness surface area and the choice is not always clear). If a business has any sort of operational component – how much to spend on employee safety tin be considered an ethical dilemma. There is a wide range of expenditure options here. The company generates revenue presumably and can spend anywhere from 0% of those revenues on safety (equipment, training, compliance expenditures) all the manner to 100% of their corporate revenues. Every bit nosotros call back nearly the craziness of either alternative, we have just entered into the Sordite's Paradox. We intuitively know that spending $0 on safety is unethical because it puts lives and livelihoods at risk. Nosotros violate the dignity of our workers by doing this. Well, so we enquire the question, what about 1% of visitor revenues on safety? Still not there? What about 2%? If nosotros take this logic all the mode to 100% we would have safety working weather condition with compliance rules in place, protective equipment, appropriate training, and what would be a waste of resources on annihilation that is not needed (you can simply spend so much on grooming before it becomes ineffective). Workers would spend more time training than working, and nosotros would accept cumbersome and unnecessary procedures that boring production. In the 100% scenario though, there is a bigger issue – we are violating the financial obligation to shareholders of the company past not working on their behalf to improve profitability in our roles every bit managers. Somewhere between 0% and 100% nosotros passed the right number to spend on safe that optimizes both safety and yet allows the business to make money. 0% violates our ethics towards employee safety, and 100% violates our ethic towards shareholder obligations. The correct answer lies somewhere in the gray area, and it is here that we run across our upstanding dilemma.
Figure 3.ii – An Ethical Dilemma Regarding Safe Expenditures
A concluding note on ethical decision making is that we generally don't start with the extremes in ethical decision making. We naturally jump right into the middle of the gray area considering we know the extremes and the fringes of the gray area are not worth pursuing. It is in the greyness expanse that we must navigate, using upstanding decision making to effigy out the best solution. We tin can achieve good determination making using upstanding frameworks.
Is the Law Enough?
Before we get to the ethical frameworks yous can apply to navigate ethical conclusion making, nosotros demand to address a common question, is the law enough to guide us in our ethics? The brusk answer is that the constabulary is an insufficient ways to regulate our ethical determination making. In that location are two primary reasons for this. First, the law gives united states of america bare minimums in terms of safety, homo dignity, and respect of rights. Even so, almost upstanding dilemmas are navigated well to a higher place these elements. For example, we are required to provide appropriate prophylactic equipment and make certain employees have condom certifications they need. Only this does not constitute the entirety of our ethical obligations in terms of condom. What is the right decision in keeping a grocery store open in a pending hurricane? OSHA has no regulation on that. However, we are putting our employees at adventure. H-Eastward-B (grocery concatenation in Texas) in Houston asked for volunteers and paid employees overtime to keep stores open so area residents. This decision went well across the safety minimums the law requires for a grocery store. Another example is that managers are required to respect the terms of a contract. All the same, the integrity of a company can be severely challenged if the focus is entirely on compliance. For example, during the 2008 financial crisis, many fertilizer manufacturers held contracts that customers bought at the top of the market. The contracts their customers entered into obliged them to pay what would get iii times the market toll after the crash. However, many manufacturers worked with their customers and renegotiated the contracts to make the customers competitive in the marketplace. This was well beyond the minimum legal requirements of the contracts. Minimum wage indicates the blank minimum your workers need to exist compensated, all the same, this does not ever equate to a living wage

in many metropolitan areas. Each of these examples highlight the need to navigate the upstanding dilemmas we face with something more than than the police force.
The second reason why the law is not a good standard is that sometimes we put in place some really bad laws. Consider the United states of america Eugenics movement in the early 1900s. We put in place laws that allowed for the forced sterilization of threescore,000 Americans that the government determined were unworthy of reproduction. This included alcoholics, criminals, intellectually disabled, and many more categorizations. Only in hindsight sometimes do we see the errors of the laws we accept put on the books.
Ethical Frameworks
Because the law is insufficient, and the nature of ethical dilemmas is one of navigating ambivalence, we need to found frameworks that volition help us make decisions. The following ethical frameworks are intended to practice that. Moral relativism offers a local solution to making ethical decisions. Utilitarianism focuses on maximizing the greatest expert for the most number of people. Justice view emphasizes the relationship betwixt members of the organization. Corporate social responsibility encourages consideration for all stakeholders affected by the decision making of an organisation. By using these frameworks equally a guide, we can begin to piece of work through a reasonable solution to ethical questions that do not take a glaring, obvious solution. These frameworks requite us structure in the gray area. Each has benefits, and faults, simply they are at least a starting betoken for establishing ethical thinking.
Moral Relativism
The construct of moral relativism holds that ethical values and judgements are ultimately dependent upon i's culture, club, or personal feelings (DesJardin, 2011). Under this framework, the right answer to the upstanding dilemma will modify based on who is analyzing the upstanding problem. Moral relativism makes the ethical decision making simple, in that the local perspective should guide the reasoning. If a manager is making a decision that is based in China, the Chinese standards of ideals should apply. If a manager is making a determination in South Carolina, every bit opposed to Alaska, the South Carolina worldview would trump the conclusion making.
There is an important distinction that needs to be fabricated when discussing the idea of moral relativism. That is, there is a significant deviation, a giant chasm in fact, between relative truth and objective truth. An example of a relative truth is something like that of an opinion – who is the greatest between LeBron James, Michael Hashemite kingdom of jordan, and Kobe Bryant. One could make the case for each of these and come to three different opinions. If I stand up and say that MJ is the all-time, this is a relative truth. This is my stance and not truthful for everyone analyzing the same decision. Mint Oreo is the best ice foam flavour. Oh, you disagree? Under the construct of relative truths that is ok. Moral relativism works perfectly fine under these weather. Examples of this would be in Colombian culture, its ok to evidence upward to social gatherings a tad (I mean a lot sometimes) fleck late. Colombians expect this. In Iowan civilisation, the expectation is that if a coming together or party is scheduled for 3pm, y'all should prove up on time, lest you offend the host. Moral relativism is an acceptable practise for cultural norms such as these. Yet, when it comes to evaluating serious ethical issues, at that place are some inherent challenges with this framework. This is sometimes called cultural relativism, and when dealing with issues of relative truths, is a mutual concern exercise.
In stark contrast to truths that change, the objective truths never change. Objective truths can also not contradict each other, otherwise one of them would be fake, rendering information technology not objectively true. Here'southward an instance: In The Hobbit (ane of the best books of all time, my relative truth), Bilbo finds the band in the cave where Gollum is hiding. Bilbo engages in a battle of riddles with Gollum, and somewhen wins the intellectual battle by asking Gollum "what's in my pocket?" (Spoiler alert) It'south the ring. At this betoken we can with certainty make up one's mind that in that location cannot be a ring in Bilbo's pocket, and simultaneously be nothing in his pocket. I of those is true. They cannot both be true. The existence or absenteeism of a ring is an objective truth. This is a metaphysical example showing that objective truths cannot contradict themselves. In the same way, if I say "there is a God" and an atheist says "no there is not," there is only one thing we can agree on and that is, merely one of us can be right.
Let's bring this distinction to the ethical framework of moral relativism. When discussing matters of ethics and the human condition, objectives truths indeed exist (as illustrated with the God instance). In the aforementioned way we should state "Human dignity should never be violated" or "human nobility should exist compromised in some situations." Both of those cannot be truthful. This ways that moral relativism can contradict itself. If something is objectively true in ane culture, it cannot be objectively untrue in another culture. In these situations, moral relativism would be useless every bit a framework for decision making.
Moral relativism has one concluding, fatal flaw. The major premise that moral relativism touts is that "no absolute truth exists." Logically, this would be that any truth that nosotros claim cannot exist absolute, significant it can simply be a relative truth. However, the premise upon which moral relativism stands is itself an absolute truth. Therefore, the statement "there is no absolute truth" cannot be truthful, meaning that absolute truth must exist.
This question has been debated for millennia from the Romans, to the Heart Historic period debaters responding to Thomas Aquina's Summa Theologie, to your high schoolhouse civics teacher preparing the fence squad for a Sabbatum see. Exploring information technology and unpacking it all here is across the telescopic of this book. Moral relativism is seriously handicapped from the aforescribed self-defeating premises. However, identifying it and illustrating the fatal inherent flaws is an important job when studying ideals because iterations and inconspicuous versions of this framework are still used in modernistic business practise.
A final note on moral relativism – in addition to the logical fallacy that it presents, there is an inherent danger in using this as an upstanding framework. If all ethical decisions are left up to the local perspective, and then even awful practices must be tolerated. This ways that we cannot condemn anything that presents a prima facie case of unethical practice. Nosotros would be unable to condemn kid labor, female genital mutilation, genocide, sex trafficking, Ponzi schemes, and the litany of other wicked practices that are accepted in some cultures.
Utilitarianism
Utilitarian ethics focuses on maximizing the greatest expert for the most number of people. Originally espoused by the English philosopher, John Steward Mill, this ethical framework provides us with a formula upon which to base our decisions. Ethical decisions should be based on the perceived outcomes they will lead to, and alternatives evaluated based on whether they volition maximize the good from the greatest number of people. Skillful tin exist defined in several ways. Good can equate to generation of money, satisfaction, life, health, opportunity, utility, and annihilation that is reasonable attributed to improving the human being status. By default, this also ways that utility maximization also avoids loss of good (loss of life, loss of money, etc.) Once the choices are evaluated and the estimated outcomes are adamant, the ethical choice is the one that creates the nigh benefit.
Utilitarianism makes upstanding decision making easy in one case the outcomes accept been projected. Will this project potentially impairment the local water source? What volition that cost in terms of clean up or quality of life? Will building a factory create jobs? After asking a series of questions like this, the outcomes are estimated to full bear on or skilful, even so that is defined in your upstanding dilemma. Notwithstanding, this ethical framework has two primary limitations. First, the concept of utility (or good) is not always hands divers. Financial analysts can project income and internet present values of decisions, and these decisions are easy to make once the numbers are in. But how do you guess how much satisfaction something volition bring? If a decision is going to result in the loss of life, how much is a human life worth? How do you gauge the impact a conclusion has on the community'south culture? Determining utility then calculating is easy in some cases, but in nigh it becomes a major claiming to using this framework. The second challenge for utilitarianism is that maximizing the greatest proficient for nigh, might result in the sacrifice of a few. A classic example of utilitarianism is the layoff decision. Nosotros need to lay off thirty people and then that the company stays solvent, and continues to provide jobs for the remaining seventy people. In this case the company stays solvent, but the xxx workers now struggle to provide for their families. Another example is a mass casualty incident. If a trauma ward is overrun with cases, the atomic number 82 md must make decisions about which patients receive firsthand care and which ones must be put aside. In this state of affairs, the doctor is trying to save the most human being life, which might issue in patients with less serious injuries accept to wait hours in pain to be treated.

Justice View
The justice view of ideals is one that endeavors to care for everyone fairly and impartially. A basic notion of justice is that we should give people what they are due. People are owed respect, dignity, civility, equity, and humanity for example. If we are trying to determine a path forward in an ethical dilemma, we would focus on these principles to decide which is the right path frontwards. If nosotros make a decision that violates these principles, then justice has been violated, and we should consider alternatives. The justice view every bit an ethical framework can exist further dissected into four specific forms – distributive justice, interpersonal justice, procedural justice, and commutative justice.
Distributive justice emphasizes equality when allocating resource. This means that individuals are given a fair opportunity to acquire resources. Resource can include salary, opportunities for promotion, benefits, favorable shifts, location preferences, and the like. To avert violating distributive justice, managers should not discriminate against individuals for the inherent characteristics which would include demographic makeup similar race, historic period, sexual practice, and all of the other categorizations that brand up protected classes in the workplace. However, we must also avoid giving preference to the all-time friend, the family unit member, the direct report who constantly flatters the director, the person who attended the same university equally the manager, and whatsoever other characteristic outside bodily performance of an individual. If, however, an individual has earned privilege through their operation, it is completely justified to provide additional resource. The top performing salesman should receive a bonus. The accountant who continually catches errors should get preferential handling for time off during tax season. The logistics scheduler who builds meaningful rapport with dispatchers should exist promotion. In each of these cases, the individual has earned the right to the resource, and distributive justice has not been violated. If we as managers take some sort of preferred method for doling resources other than what people have earned through their performance, we are violating distributive justice.
Interpersonal justice an ethical framework that focuses on the advice within a relationship. The essence of this justice view is that the fashion in which we communicate determines whether or non justice has been violated. Talking to people with disrespect, belittling, coercing, or beingness rude or uncivil in a delivery of a message all establish interpersonal justice violations. Consider the post-obit ii scenarios. Scenario #ane: Beck has continually underperformed to the signal where the managing director has determined that she should be terminated. The manager sits down with Brook and calmly explains the consequences of her performance, wishes her well, and on the way out the door offers a reference to her for a job opportunity. Brook is not happy about losing her task, only she does not feel like interpersonal justice has been violated. Scenario #2: Otto works as a toll accountant and recently performed in a higher place his peers during a mill expansion project. As a result, the bookkeeping manager has rewarded him with two tickets to the Milwaukee Brewers game. As the manager hands Otto the tickets he says, "I know that if accountants don't become out of the office, they will whine almost information technology, then hither are two tickets." In this scenario, Otto earned the prize and then distributive justice was not violated. Notwithstanding, the manner the manager treated him makes him feel disrespected, a clear violation of interpersonal justice.
We have this unstated expectation that we should be treated with dignity. This is why any form of sexual harassment immediately elicits an indignant response. Information technology violates the interpersonal justice view that we should not be talked to, or treated in a way counter to decency and our humanity. When we are treated with disrespect in the workplace we resent the manager or the organization in that moment, and if this happens oftentimes enough, inquiry shows that it volition affect our own functioning, and the operation of the organization (Estes & Wang, 2008). In short, avoid disrespecting people and you will maintain interpersonal justice.
Procedural justice follows that every bit long as the protocols and rules are followed, procedural justice has non been violated. If the organization gives out promotions based on how long someone has been at the organization, and this is a clearly established rule, procedural justice would not be violated within this context. It might be the case that we disagree with this rule considering beingness at an organization a long time does not make you good at something (similar tenure at a university, high school teachers, military promotions), simply as long as it is an established rule, no one will feel that procedural justice has been violated. Another instance of procedural justice is the fashion in which people are evaluated for their work. At a customer service call center, companies oft evaluate their employees based on a set of standard metrics. Everyone knows them, there are clocks on the wall to measure them, and at the end of the evaluation menstruation, everyone knows what to wait. These include metrics like how long calls last, did the agent resolve the issue, and did the customer have to call up later to ask more questions. Once again, some of these are measures that could be improved, and we might disagree with them, but the rules are being followed so procedural justice wins. Consider the example of a professor who has established a rubric for the midterm paper. It has been posted on the Blackboard site, and information technology was communicated well earlier the assignment was due. The students piece of work on the paper, submit them, and receive an evaluation that falls outside the rubric metrics. The professor had not included spelling and grammar as part of the rubric, but during the grading of the papers, he hammers the students on this bespeak. The students will feel that procedural justice has been violated because the rules (in this case an established rubric) were not followed. Under procedural justice, what the rules are practise not thing. Whether they were followed do matter.
Finally, commutative justice is a form of justice that is determined based on all parties having full cognition of the relationship or transaction. Consider the classic case of going to a machine dealer, and upon going to sign the papers, y'all detect a charge for a warranty that you had non agreed to. The salesman put this in the contract without you lot asking. Immediately you go upset that the salesman tried to pull 1 over on you. You were not given all of the data in the transaction, and therefore commutative justice has been violated. Another scenario where this normally occurs is in costless trials for online services. Yous sign up for a seven day trial, and at the terminate of the trial menstruum, the company charges yous for the full service because yous did not call to abolish. If an system has identified some particular dangers, they should alert the employees to the danger then that they can make an informed decision regarding their employment. An example of this is crab angling in the Bering Sea. Captains brand the dangers very articulate to people who want to become fisherman and every bit a result, commutative justice is non violated. For this aforementioned reason, if you decide to go skydiving, you have to sign an acknowledgement of risk, and waiver of liability before they will permit you skydive. The risks include death, cleaved ankles, heart attack, and paralysis. The skydiving companies are making the risks clear so that they do non violate commutative justice.
The expert news hither is that the law is on your side. It would be unlawful for someone to include terms within a contract that the other party was unaware of. Additionally, the linguistic communication within the contract has to be written in a way that a reasonable person tin understand information technology. In the absence of these factors, the court has upheld that some terms inside contracts are not enforceable. These clauses violate commutative justice considering we take a right to know what we are agreeing to.
Corporate Social Responsibility
Finally, an ethical framework that has gained in popularity in the terminal two decades is corporate social responsibleness (CSR). CSR is an ethical framework that takes into consideration all of the stakeholders that are impacted past a business decision. This ways that in improver to because the financial stake that shareholders take in an organization, the employees, communities, creditors, suppliers, environment, and authorities should also be included in the consideration of conclusion making. Klein (2012) states that "every corporation has an overarching social purpose that transcends the operations of corporate social responsibility and, when well understood and finer integrated, tin accept profound business and social results" (para four). The underlying premise with CSR is that business organisation demand to exercise more than simply make money. They need to advance the agenda of the social proficient besides. Other names for this approach include the triple lesser line and balanced scorecard, whereby companies report on their impact on profit, planet and people (Spreckley, 1981).
Let's go dorsum to the outsourcing case. If we consider this decision a greyness area ethical dilemma, we can use CSR to consider how to move forward. An assay might these questions: What is the profitability of outsourcing our product (shareholders)? How much should we pay in severance to domestic workers (employees)? What is the economic impact on local town where manufactory will close (customs)? What economic benefit volition the factory in the new country bring to its local community? Are we violating any U.Due south. laws with our labor practices in the new state (government)? What is the impact on our supply chain and vendors (suppliers)? And the listing goes on. CSR as an ethical framework forces companies to think through all stakeholder groups as they make decisions. What should be articulate as a downside to this ethical framework is that sometimes stakeholders have competing interests. Your decision to motion abroad helps the new town, only hurts the old. It has profitability potential, only might require you to employ a new supplier or creditor, forcing them to detect new business concern. This is the main criticism with CSR, but the overall idea with this framework is that we demand to at to the lowest degree exist asking the questions about each group as we make decisions.
The origins of CSR come from a classic view of business that profits come first. In the 1970s, Milton Friedman famously stated that businesses have only one purpose and that was to maximize wealth for the owners. He offered that by taking care of owners, they would past default be taking care of society by virtue of providing jobs for employees, who would and then exist providing economical growth for society, etc. In the 1980s, this idea was challenged by Edward Freeman, who established stakeholder theory – the founding idea for what nosotros phone call CSR today. Since and so many businesses accept gone beyond simply focusing on profits and have established clear missions on creating social value
CSR has been the focus major corporations and researchers alike over the last ii decades. Much of this emphasis has been placed on a related concept of sustainability, which entails the responsible and efficient use of the earth's natural resources. Sustainability in recent years has also expanded to enscope social and economic variables too – treating each of the resources in these domains as resources that require attending, diligence, and consideration.
Critical Thinking Questions
Which element of the conclusion making procedure is the most important to get right? Why?
Which upstanding framework makes the most sense? Why?
Why is the law not a sufficient standard to use equally our upstanding guide?
For each of these answers you should provide three elements.
- Full general Answer. Give a full general response to what the question is asking, or make your argument to what the question is asking.
- Outside Resources. Provide a quotation from a source outside of this textbook. This can be an academic article, news story, or popular press. This should be something that supports your statement. Utilise the sandwich technique explained below and cite your source in APA in text and then a listing of full text citations at the finish of the homework consignment of all three sources used.
- Personal Story. Provide a personal story that illustrates the bespeak every bit well. This should be a personal feel you had, and not a hypothetical. Talk about a time from your personal, professional, family, or school life. Utilize the sandwich technique for this too, which is explained below.
Employ the sandwich technique:
For the outside resources and the personal story you should use the sandwich technique. Good writing is not just about how to include these materials, but nigh how to make them menstruum into what y'all are saying and really support your argument. The sandwich technique allows usa to do that. It goes similar this:

Step ane: Provide a sentence that sets up your outside resources by answering who, what, when, or where this source is referring to.
Step 2: Provide the quoted material or story.
Stride 3: Tell the reader why this is relevant to the argument you lot are making.
Chapter References
J., O'Rourke, J., Parboteeah, P., Pierce, J., Reece, 1000., Shah, A., Terjesen, South., Weiss, White, 1000. (2019). Principles of Direction. Rice University, Open Stax: Houston, TX
DeJardin, J. (2011). An introduction to business ethics (4th ed). New York, NY: McGraw Hill.
Estes, B., & Wang, J. (2008). Integrative literature review: Workplace incivility: impacts on
individual and organizational functioning. Homo Resources Evolution Review, 7(ii), 218-240
Hannaway, J. (1989). Managers Managing: The Workings of an Administrative Organization. New
York: Oxford University Press, P. 39
Klein, P. (2012). Defining the social purpose of business. Forbes Online. Retrieved
from https://www.forbes.com/sites/csr/2012/05/14/defining-the-social-purposeof-business/#14e2188b1cac.
Lussier, R. (2021). Management Fundamentals: Concepts, Applications, Skill Development. (9th
Ed). Sage Publications: Yard Oaks, CA.
Nourse, 5. (2016). When eugenics became law: Victoria Nourse reviews a study on a
celebrated Us misuse of biology, the case of Buck V. Bell. Nature, 530(7591)
Spreckley. F. 1981. Social Audit: A Management Tool for Branch Working. Leeds, United kingdom:
Beechwood College.
hardydideenable94.blogspot.com
Source: https://fhsu.pressbooks.pub/management/chapter/ethical-decision-making/
0 Response to "Explain Your Ethical Decision Making Process When Determining Your Answer Regarding Baby M"
Post a Comment